Micro Loop
OSPF Loop
Loop occurrence is a common issue at Layer two and three. Let us focus on layer three in this article. Routing loops can get identified when we try to ping the destination by receiving the ICMP message, “packet expired in transit”.
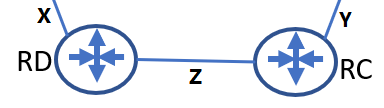
Let’s have a simple topology to understand it better.
The router “RD” has a forwarding entry point to the neighbor router “RC” to reach the segment “Y”, presume that “RC” lost the connectivity to segment “Y”, which is on in it. However, there is an update coming from “RD” (the entire route database), “RC” sees that there is the path to reach the segment “Y” through the neighbor router “RD”; therefore, “RC” will update its routing table accordingly. “RD” had learnt this update from “RC” in the earlier route exchange process. Let’s see the issue here, A datagram coming from the Segment “X” to “Y” has to go through “RD” and “RC”. Hence, “RD” will forward the datagram to “RC”. “RC” will send it back to “RD” because “RC” believes the segment “Y” can be reachable through the neighbor “RD” it goes on and on until the TTL expires.
The duration of this problem may depend on the protocol that is in use. RIP will rip us into two and, OSPF will tackle by itself with its intelligence. The concern while the problem is surfacing what happened to the sensitive data. How it occurs in the OSPF, let’s take this topology.
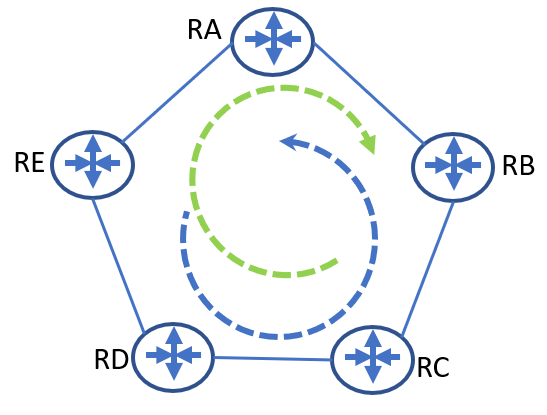
Topology
Topology explanation:
Five routers connected each other in the topology; the green dotted circles illustrate the actual route path; the blue dotted circle shows an alternate route path in case of link/router has broken.
Device Connectivity
It means, “RA” -> “RB”, “RB” -> “RC”, “RC” -> “RD”, “RD” -> “RE”, and “RE” -> “RA”.
Assume “RA” lost its link that goes to “RB”, “RA” will switch to its alternate path to reach “RB“ through “RE”, so far “RE” knows to orbit to “RB” through “RA”. In this instance, the datagram will get ping ponged between “RE” and “RA”. However, this loop will get mitigated by the OSPF protocol itself because of the trigger update feature. However, there is a loop for some microseconds, which is called “micro-loop”.
Why do we need to concern about it, when it is going to surface for a few microseconds?
When Smart-city CCTV camera data goes back to the Media Server. When healthcare medical instruments communicating with one another.
It is important give thought about it!